[ad_1]
What are Dependencies?
In computer science, a dependency occurs when one component (class, module, etc.) relies on the functionality of another component to operate correctly. For example, a Laptop component depends on a Battery component to provide power.
\
\

Dependency Injection
Dependency Injection (DI) is a powerful technique that helps manage dependencies between components. Instead of a component directly creating the objects it depends on, those dependencies are provided (“injected”) from the outside.
\
This leads to several key benefits.
\
Consider the Laptop and Battery scenario. Here’s a contrast between traditional instantiation and using Dependency Injection:
\
\

\
\
\
\
Advantages of Dependency Injection:
-
Improved Testability: DI makes unit testing a breeze. You can easily replace a real dependency with a mock or stub during testing, allowing you to isolate the component you’re testing and focus on its specific logic.
\
-
Loose Coupling: Your classes don’t have to be tightly bound to specific implementations of their dependencies. This means pieces of your code become more independent, leading to better maintainability.
\
-
Flexibility: You can easily change the underlying implementations of dependencies without breaking the classes that use them. For example, switching from a database logger to a file logger becomes a simple configuration change.
\
-
Reusability: Since components are not responsible for creating their dependencies, they become more reusable in different contexts.
Disadvantages of Dependency Injection:
-
Increased Complexity: Introducing DI, especially when done manually, can add a layer of complexity to your code with more classes and interfaces to manage.
\
-
Boilerplate Code: Some DI setups can involve writing a decent amount of code for object creation and dependency wiring, though this can be mitigated with DI frameworks.
\
-
Overuse: It’s possible to overuse DI, even in cases where it provides minimal benefit. This can lead to unnecessary complexity.
When to implement Dependency Injection in Your Project?
- Testability: When you prioritize extensive unit testing, DI is a godsend, allowing you to isolate components and test them independently.
\
- Flexibility: If you anticipate needing to swap out implementations (like switching databases, logging mechanisms, or external services), DI provides a seamless way to do so.
\
- Long-term maintainability: When you want to minimize the ripple effects of changes, making your code more robust over time, DI fosters loose coupling and promotes long-term health.
\
- Code reusability: If you want to write components that are highly reusable in different contexts, DI keeps them free from directly managing their dependencies.
Types of Dependency Injection
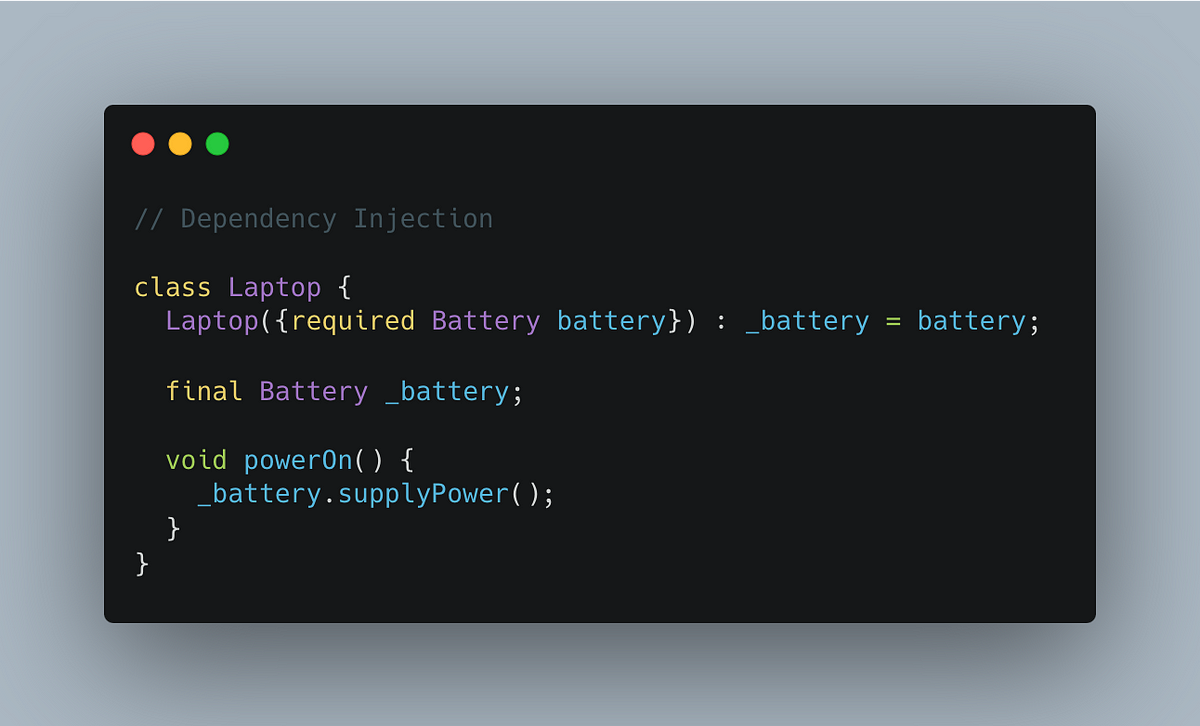
1. Constructor Injection
\
\

\
\
How it works:
- The Laptop class requires a Battery dependency to be provided when it’s constructed. This ensures the Laptop always has a functional battery.
\
2. Setter Injection
\
\

\
\
How it works:
- The Laptop can function without a battery initially.
\
- The battery setter method allows you to inject the dependency later.
\
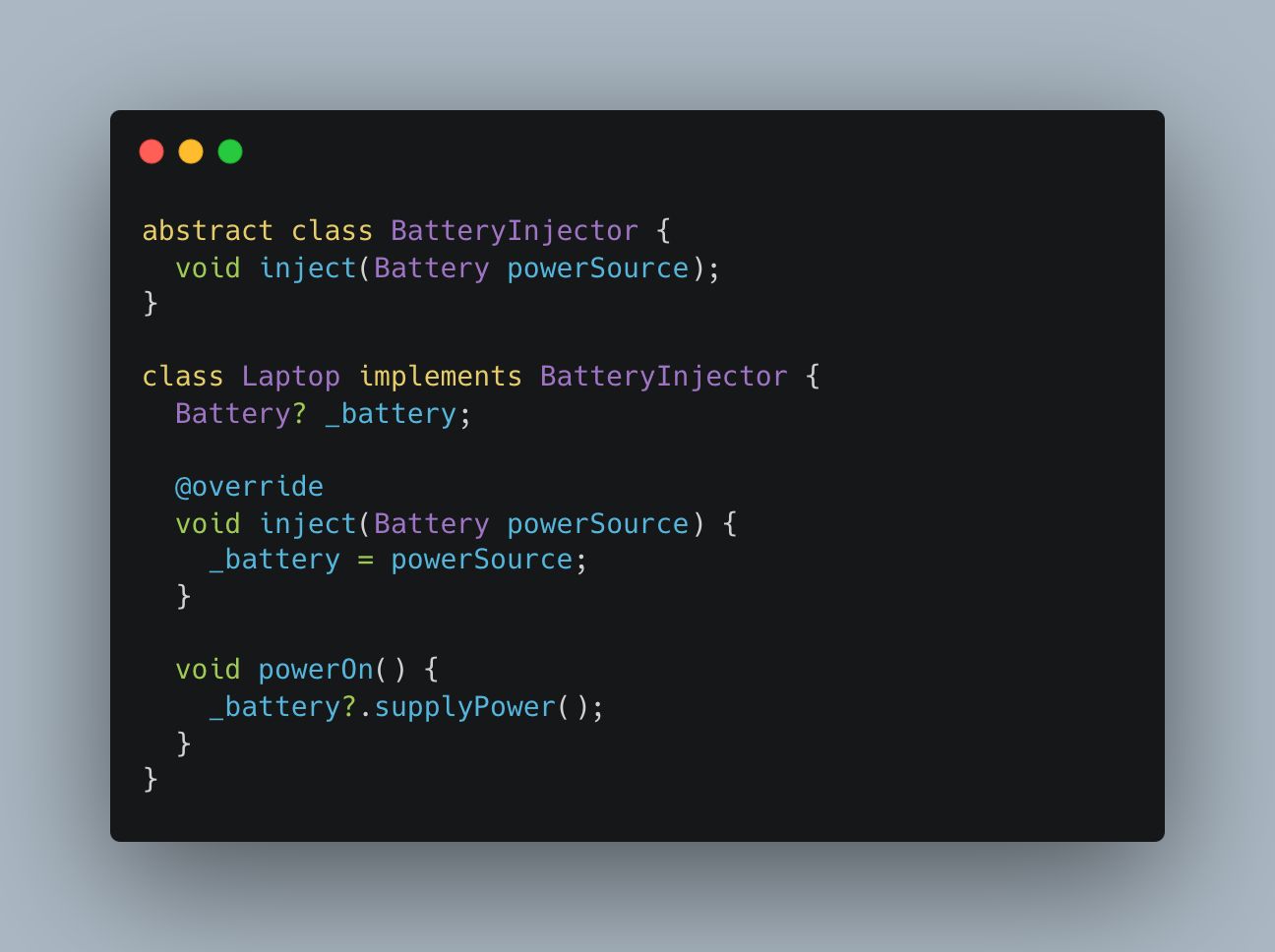
3. Interface Injection
\
\
\
\
How it works:
- An external injector would call inject to provide the battery.
Additional Considerations & Techniques
1. Ambient Context
\
\

\
\
How it works:
- A global class AmbientContext acts as storage for dependencies.
\
- Before use, the context is initialized (e.g.,
AmbientContext.initialize(batteryInstance)).
\
- The Laptop class retrieves the Battery dependency directly from the AmbientContext when needed.
\
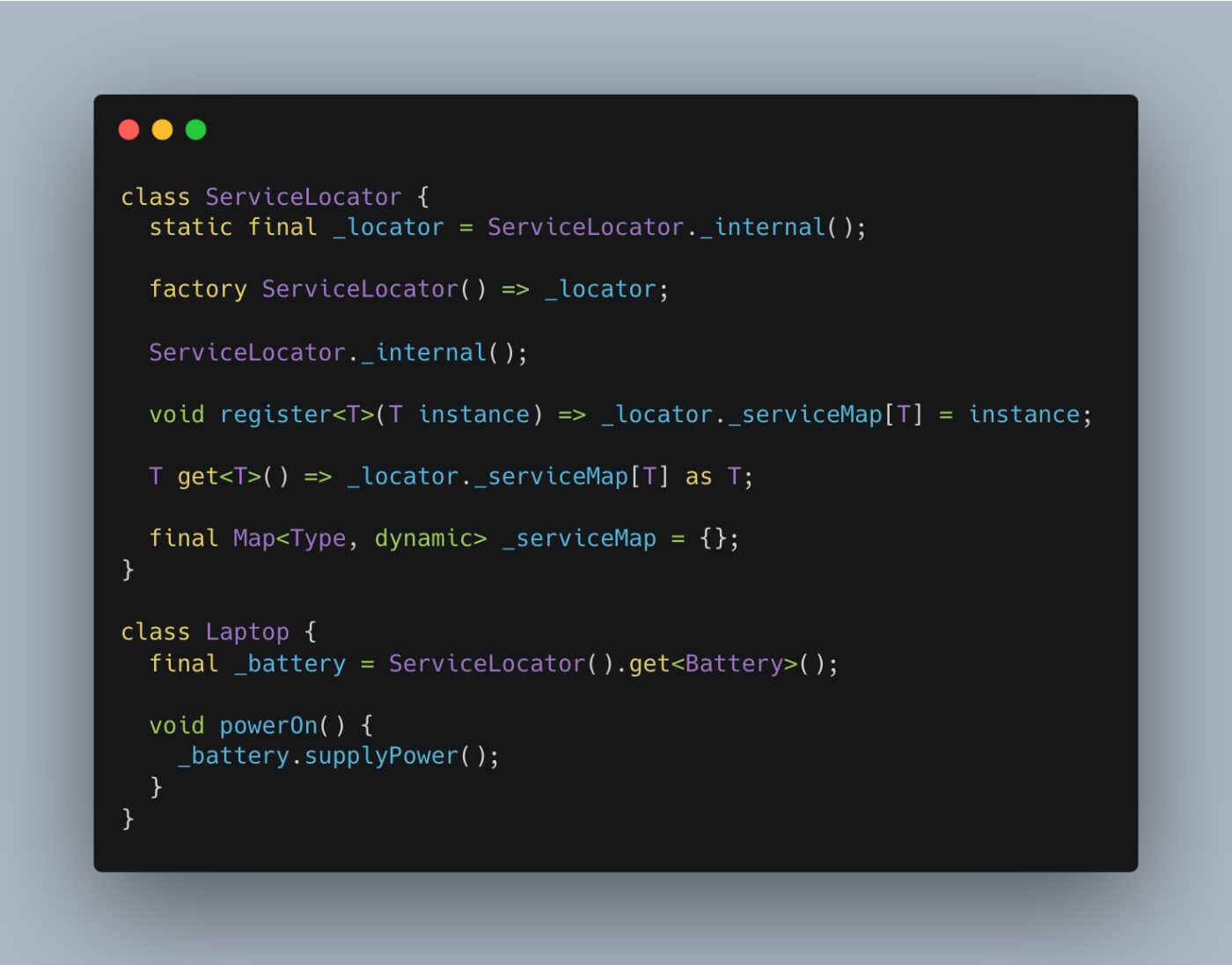
2. Service Locator
\
\
\
\
How it works:
- A ServiceLocator class acts as a central registry for dependencies.
\
- Dependencies are registered with the locator (e.g.,
ServiceLocator().register<Battery>(batteryInstance)).
\
- The Laptop class queries the ServiceLocator to retrieve the Battery dependency when needed.
Also published here
[ad_2]
Source link

